Immunotherapy is a kind of treatment that boosts a person’s immune system to fight cancer. The immune system is majorly made of white blood cells, tissues, and organs of the lymph system. In a healthy human being, the immune system prevents the growth of various kinds of cancer by finding and destroying abnormal cells. For example – The cells of the immune system are found inside or around tumors in the body which means that the immune system is affecting the tumor. These immune system cells are called TILs or Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. People whose tumors have these cells do better than those compared to who don’t have them. Though our immune system can destroy slow cancer-growing cells, some cancer cells find ways to avoid this. For this, the cancer cells might have the below possibilities.
Various kinds of immunotherapies are used to treat cancer.
These are drugs that block immune checkpoints, thereby allowing the cells of the immune system to respond more strongly and vigorously to cancer.
This is a therapy that boosts the ability of the T Cells to fight against cancer. Immune cells, that are active against cancer are taken from your tumor. These are then grown in large batches and put back into your body through a needle. This therapy is also called Adoptive cell Therapy, Immune Cell Therapy, or Adoptive Immunotherapy.
These are the proteins of the immune system, created and designed in a lab to bind to certain targets on the cancer cells. Certain monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells allowing the immune system to see them better and destroy them. These antibodies are another type of immunotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies are also called therapeutic antibodies.
These are vaccines that boost your immune system to act against cancer cells. These are different from the kind that helps to prevent diseases. Immunotherapy is given in different ways.

Precision medicine is the new medical model which has become very popular in just over a decade. It is the elaboration of the methodology which believes that one treatment doesn’t fit all. Therefore, it can be described as customization of healthcare with tailored medical decisions, treatments, practices, or products by using the molecular information, phenotypic, and health data from a specific group of people to establish care insights, and prevent, or treat them in such a way that their health outcomes are improved.
In simple, giving the right medicine, to the right patient, at the right time.
Precision medicine sometimes can also be called personalized medicine, is carried out by understanding the genetic molecular mechanism of diseases, thus helping in deriving, which treatments work well with which group of patients. It is because of the observation of patients with the same type of clinical diagnosis or symptoms responding in different ways to similar treatment.
Hence, by knowing the patient’s characteristics (biomarkers) and grouping them; specific types of treatments, therapies, preventive diagnoses, and other health measures can be generated.
An individual’s genome is identified and sequenced by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), an important advancement in the clinical applications of precision medicine.
Doctors, patients, and researchers can use this NGS to identify genetic variants that help diagnose, treat, and learn more about human diseases.
There are 2 types of drugs under Targeted Therapy
These can enter the cells very easily enabling them to interfere with the inside molecules. These can also be used against molecules on the cell’s surface.
These work outside the cancer cells as they are larger. They target those molecules that are on the surface of the cancer cells. They are designed using cloned cells which produce antibodies that interfere with the molecules that are targeted. These are also used to deliver toxic molecules into the cancer cells directly.
In the future, if there is a complete understanding of the secret behind a patient’s genetics and its impact on his underlying condition or the likeliness of developing such condition will be a phenomenal achievement in revolutionizing the approach to medical practice.
VATS (Video assisted thoracoscopic Surgery) is a procedure that is used by the doctor to examine the inside of your chest cavity and the lungs. This is used to diagnose and treat health problems inside the chest and the lungs.
It is performed with the use of a thoracoscope, which is a narrow, thin tube with a camera at the end.
Below are the reasons for using VATS
VATS is a very good option for people who cannot go for an open chest surgery because of previous chest surgeries or have other health issues. Your doctor will suggest if you can go for VATS or not.
VATS falls under the minimal invasive surgery and involves various types of procedures.
This is where one of your lobes of the lung is removed through surgery. This is a common treatment option for non-small cell cancers of the lung.
This is another procedure for patients with lung cancer, where a small, triangle shaped part of your lung (a Wedge) is removed.
This is a process where the side of your chest is opened to access the pleural cavity. This is the space under the chest wall, between your lungs.
This VATS procedure (Pleural effusion) is done to remove the fluid build-up from the pleural cavity.
A small amount of tissue is removed from your body and a close examination is done to find cancer cells. If there are cancer cells, a VATS biopsy is done.
Just before the VATS procedure begins, you will be given general anesthesia. You will be asleep all during the procedure so that you don’t feel pain. A breathing tube is inserted for you to breathe normally.
Your body is positioned to the side helping the surgeon make small cuts near the ribs, on your chest. Then, the thoracoscope is inserted into these incisions to enable the surgeon see inside the body to perform the procedure.
During the time of recovery, you might take a little more time to feel normal again. So, it is good that you follow your doctor’s instructions and take enough rest.
VATS offers fewer complications and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
It is very common that you will feel sore at the places of incision on your body. But there is nothing to worry. These incisions are closed with either stitches or staples, which will be removed by your doctor during your follow-up visits.
You will also feel tired for few days. So, follow the after-care instructions and take medicines regularly.
After you start begin to feel normal, you can do some gentle exercises. Stay away from heavy workouts.
If you not feeling well during your recovery, you can always call the care team.
Oncoplastic Breast Surgery offers the combined techniques of traditional breast surgery and plastic surgery. The ultimate goal of this treatment is to minimize the side effects and promote physical and emotional healing.
This treatment is a blend of oncoplastic surgery and Lumpectomy. The surgeon will remove the tumor, nearby lymph nodes, and a small amount of the surrounding tissue. Then the bilateral breast reduction or lift is performed towards symmetrical breasts.
Depending on the characteristics of Cancer, there are many oncoplastic techniques. The most common are listed below.
Local Advancement Flap: Using traditional lumpectomy, doctors remove the tumor and a little portion of the surrounding tissue. Thereby, depending on the location and size of the tumor, this will deform the breast. Using a local advancement flap, surgeons take the tissue that remains after the tumor removal. This is used to reconstruct the appearance of the normal breast. This ensures that there are no defects.
Bilateral Breast Reduction: If a lumpectomy is done to one breast, its size and shape can alter. But bilateral breast reduction is a solution for this as it alters the shape and size of the other breast too.
This process involves removing a large amount of tissue from the other breast, which can be helpful as additional tissue in the case of a large tumor. Modification in the other breast ensures both breasts look symmetrical.
Bilateral Breast Lift (Mastopexy): This is a kind of minimal bilateral breast reduction treatment. This is the right option for those who do not want to reduce their breast sizes. This treatment is also called Mastopexy. Instead of removing large amounts of tissues from both the breasts, the tissue is removed from the affected breast and an equal amount from the other one. This will ensure more symmetrical breasts.
Skin-Sparing Mastectomy: This is a kind of treatment that is necessary for patients with advanced stages of breast cancer. Skin-sparing Mastectomy helps in conserving the look of the breast.
This procedure involves the removal of the skin of the breast, nipple, and areola. The breast tissue is then taken out, after which the surgeon reconstructs the breast using the removed skin. This will make sure that the original appearance and shape are restored.

At Kaizen Oncology Network, we bring together a multidisciplinary and distinguished team of physicians, surgeons, and other care professionals to preserve the organs that are vital for your life or that cannot be easily replaced. There are multiple organs that can be preserved and the purposes are varied as per the treatment, surgery, and recommendations from the doctor.
Techniques for organ preservation serve to minimize the damage of surgery in and around the targeted area to promote optimal graft survival and function. The main goal in organ preservation is to maintain the function of the organ and tissue during storage so that the graft will function at re-perfusion.
This is a surgical procedure that is done to rebuild the shape of the breast. This procedure is common for women who had undergone surgery for the treatment of breast cancer.
Usually, breast cancer surgeries are performed to remove cancer and leave normal breasts to the most extent possible. But in advanced cancer, the procedure involves removing all of the breast tissue. These cases require breast reconstruction surgery to rebuild the appearance and shape of the breast.
Sphincter preservation surgeries are the recommended treatment option for low rectal cancer which is traditionally treated with abdominoperineal resection (surgery in which the anus, rectum, and sigmoid colon are removed).
A sphincter preservation surgery involves complete resection of the tumor by preserving the continuity of the bowel and functioning of the anal sphincter.
Sphincter preservation surgery is an acceptable alternative to abdominoperineal resection for low rectal cancer, offering a better quality of life and sexual-urinary functions, with no increased oncological risk even after 3 years
Bladder preservation is not only very safe but also effective for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Surgical removal of a part or complete urinary bladder requires urinary diversions and substantially weakens the patient’s quality of life. This procedure is a way of treatment for cancer without affecting the bladder’s function or form. This approach is usually a combination of three different treatments.
Patients living with cancer, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, or a non-healing wound on the leg, are at a high risk of limb amputation. Latest advances in limb-sparing surgery have enabled physicians to help you to keep your limb. The procedure is performed to either remove limb tumors or to manage the wound without removing the whole limb. At Kaizen Oncology Network, we focus to preserve your limb(s) while offering you a lifestyle of independence and mobility.
At Kaizen Oncology Network, we are committed to providing the most advanced surgical and medical treatment to all our patients with access to the latest treatment and technology available. The staff at Kaizen Oncology Network aims at providing the best care and quality service in a pleasant ambiance. We offer a wide range of latest technology services along with competent and highly experienced doctors and staff. We are among the best oncology hospitals that offer quality patient care with an ethos of Safety.

BMT (Bone Marrow Transplant) is a treatment for people who have blood cancers like Leukemia or Lymphoma, and disorders of the blood like sickle cell disease.
A BMT is a treatment option where unhealthy blood-forming cells are replaced with healthy cells. Red blood cells, White blood cells, and Platelets are all blood-forming cells (Blood Stem Cells). These are found in the soft tissue of the bone called Bone Marrow. After these cells become mature, they enter the bloodstream leaving the bone marrow.
Before a bone marrow transplant, you receive Chemotherapy, or sometimes Radiation therapy too, so that the diseased cells and Marrow are destroyed. After this, healthy cells are given to you.
Though the BMT procedure is complicated and challenging, it doesn’t involve surgery but begins with the recipient receiving peripheral blood stem cells from the donor. In another method, Marrow cells are collected from the back of the pelvic bone using a syringe during which the donor is given general anesthesia.
There are 3 sources of getting healthy cells.
There are 2 types of BMT
Your BMT doctor will suggest you the right kind of transplant and the sources based on certain factors like
A BMT treatment requires time for a lot of planning. So, your doctor will possibly start the process early. Generally, transplants show success rates if
More than 70 diseases can be treated by BMT which also include
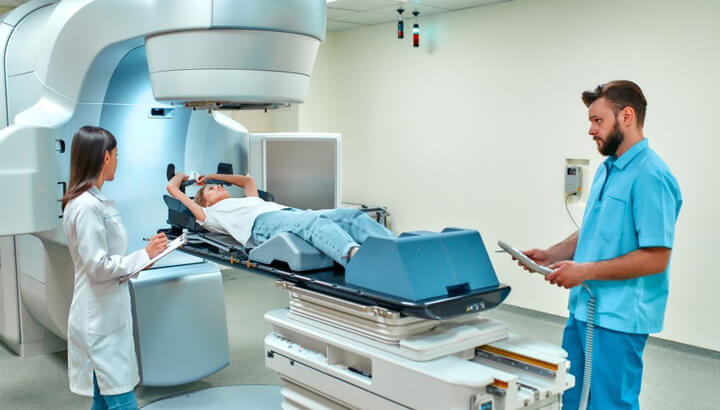
IGRT (Image Guided Radiation Therapy) is a treatment procedure which uses imaging technologies like MRI, PET and CT to safely deliver accurate radiation on cancer cells. The machine that is used to deliver radiation is called linear accelerator. These machines are equipped with imaging equipment to enable the doctor to exactly find the tumor before and while treatment.
The most commendable benefit of GRT is being very precise, that enables possibilities like
At the beginning of every session of treatment, you will be positioned on to a treatment table. Various scans are conducted to ensure that your body is positioned right. More scans might also be taken just to ensure that the radiation is delivered on to the targeted area. IGRT procedure might consume longer time than other types of radiation treatments.
MRI, PET and CT imaging technologies are used during and before IGRT, to make sure that the treatment is safe and precise. During some IDRT procedures, small dots (Fiducial Markers) might be placed on your body close to the tumor, for locating the cancer.
These imaging technologies are used to constantly monitor the tumor to check for growth, shrinkage or any changes in the shape of the tumor.
You will require multiple sessions of IGRT. Usually, IGRT is done 5 days a week stretching for several weeks. The total number of treatment sessions depend on different factors like the type of cancer, its location and size of the tumor.
IGRT is usually used to treat tumors that are located in or close to sensitive organs in the body. IGRT is apt for those tumors that might move during treatment or between sessions, like lung tumors.
IGRT is generally used to treat lung cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, spine cancer, brain cancer, bladder cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, bone cancer and also for lymphoma.
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a highly meticulous form of radiation therapy that was developed to handle small brain tumors and their abnormalities. Though the name includes “surgery”, it is a minimally invasive non-surgical procedure that delivers high doses of radiation to the pinpointed targets. Great advancements in radiation technologies allow the delivery of the pre-decided high doses to the targeted tissues while minimizing the dosage and effect on surrounding healthy tissue.
SRS delivers a methodical, systematic, safe, and minimally invasive treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with malignant, benign, and specific dysfunctionalities of the brain and spine including primary and secondary tumors. SRS can also be effectively deployed for most metastases, meningiomas, schwannomas, pituitary adenomas, and arteriovenous malformations.
The SRS team is mostly comprised of a radiation oncologist, medical radiation physicist, radiologist, dosimetrist, radiation therapist, and radiation therapy nurse.
The complaints or side effects are temporary. They are:
Copyright © 2022 kaizen rights reserved.